Is The Golgi Body In Plant Or Animal
Quick expect: Golgi appliance(or complex, or torso, or 'the 'Golgi') is found in all plant and brute cells and is the term given to groups of flattened disc-similar structures located shut to the endoplasmic reticulum.
The number of 'Golgi appliance' within a cell is variable. Animal cells tend to have fewer and larger Golgi apparatus. Establish cells tin contain as many every bit several hundred smaller versions.
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins and lipids (fats) from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Information technology modifies some of them and sorts, concentrates and packs them into sealed aerosol called vesicles. Depending on the contents these are despatched to i of three destinations:
Destination 1: within the prison cell, to organelles called lysosomes.
Destination 2: the plasma membrane of the jail cell
Destination 3: exterior of the jail cell.
The proper name behind the appliance
The Golgi apparatus is the simply prison cell organelle to exist named after a scientist. The visible characteristics of the organelle were first reported by Camillo Golgi (1843-1926) at a coming together of the Medical Society of Pavia on 19 Apr 1898 when he named information technology the 'internal reticular apparatus'.
Contend nearly the existence of the apparatus continued even later on 1913 when the term 'Golgi apparatus' was officially given to the 'internal reticular apparatus'. Information technology was not until 1954 that work in electron microscopy finally put the seal of approval on the existence of the organelle and the eponym 'the Golgi', was fully accepted.
Going for Golgi. Where is the Golgi apparatus and what is information technology?
Where is it?
Golgi appliance is present in eucaryotic cells equally ane or more groups of flattened, membrane-bounded compartments or sacs. They are located very nigh the rough endoplasmic reticulum and hence near the nucleus.
What is it?
The compartments of the Golgi appliance await rather like a pile of Pitta breads with the i at the height and bottom not existence shine but having broken open up outermost surfaces. The number of compartments in any 1 Golgi apparatus is ordinarily between 3 and viii. The number of sets of Golgi apparatus in a cell can exist equally few as ane, equally in many creature cells, or many hundreds as in some constitute cells. Specialised secretory cells contain more than sets of Golgi apparatus than do other cells.
The Golgi apparatus is function of a manufacturing and supply chain
In non-biological terms the Golgi apparatus tin be divided into 3 chief sections:
1) Appurtenances inwards
2) Main processing area
3) Appurtenances outwards
-
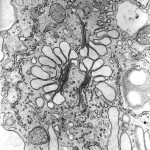
In the center of this image from a maize root cap slime-secreting cell at that place are ii Golgi stacks. The large white sacs near them incorporate mucilage produced by the Golgi apparatus.
(courtesy of Chris Hawes, The Research Schoolhouse of Biology & Molecular Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, UK)
In terms of cell biological science these sections, working from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) outwards, are as follows:
i) Cis Golgi network (Goods inwards)
Likewise called the cis Golgi reticulum it is the entry surface area to the Golgi apparatus. It follows the 'transitional elements' which are smooth areas of the RER that are also known as the 'endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartments' (ERGIC).
2) Golgi stack (Main processing expanse)
This section is composed of a variable number, typically 3-6, of flattened sacs called cisternae (sing. cisterna). The cisternae of the Golgi stack are divided into three working areas: cis cisternae, medial cisternae and trans cisternae.
3) trans Golgi network (Goods outwards)
This section is directly continued to the trans cisternae and information technology is here that final reactions and sorting takes place. The concentrated biochemicals are packed into sealed droplets or vesicles that grade by budding off from the trans Golgi surface. The vesicles are then transported away for apply in the cell and beyond.
Golgi apparatus – what does it practise?
The Golgi apparatus is rather like a food supermarket with an in shop bakery. Information technology takes in products from the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) in what is called 'bulk menstruation' (the equivalent of a bulk delivery to the supermarket). These chemical products are transported to the Golgi apparatus in sealed droplets or sacs called vesicles and move to a 'deliveries only' part of the Golgi apparatus.
In the Golgi apparatus the vesicles are delivered into the 'unloading bay' of the cis Golgi network. Hither the 'goods received' are checked over. Whatever goods that have been wrongly delivered, including chemicals that should have stayed in the RER, are sent back, packed in vesicles to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The proteins and lipids that take been correctly delivered are then passed into the cisternae of the Golgi stack and processed and sorted in an orderly sequence co-ordinate to any 'labels' they bear. Some of the items from the rough endoplasmic reticulum go to the equivalent of the supermarket in store bakery and are converted into other products and re-labelled. In plants for example equally much as fourscore% of biochemical activity in the Golgi cisternae can exist devoted to producing chemicals such as pectin and polysaccharides used in making cell walls.
The correct 'labelling' of products is critical. Inclusion cell (or I cell) disease, an inherited lysosome storage disorder in humans, is caused by a metabolic labelling error. The error causes chemicals to be despatched to the prison cell surface and secreted whereas the correct labelling would take despatched them to lysosomes. The lysosomes then accumulate material that should have been broken down. This accumulation causes the disorder.
Moving through Golgi or Golgi moving?
The style in which chemicals move through the Golgi apparatus from cisterna to cisterna is not fully resolved. One idea is that a new cisterna forms at the cis end (the end nearest the rough endoplasmic reticulum) then changes equally it moves abroad from the RER becoming in time the trans end. A more accepted idea is that chemicals being processed in the Golgi apparatus travel from one cisterna to another in ship vesicles or peradventure along microtubules. Whatever the transport method, what is articulate is that unlike chemical reactions accept identify in especially designated parts of the Golgi appliance.
Golgi biochemicals. Where exercise they go? How do they go there?
There are three main destinations for biochemicals released from the trans Golgi network: (one) within the prison cell to the lysosomes; (2) the plasma membrane and (3) outside of the cell. In each case the destination is clearly linked to function.
Using the food supermarket illustration, all the biochemicals transported away from the trans Golgi network have labels and barcodes built into them. They are all packed in vesicles and the construction of the vesicle or vessel is largely related to the vesicle contents, its destination and end employ.
Destination 1: inside the jail cell, 'the lysosome line'
About 40-50 different biochemicals despatched from the Golgi apparatus in vesicles are destined for delivery to the lysosomes. Beast cells comprise many lysosomes and it is in these structures that some life expired organelles and other materials are digested (come across item CU9 nearly lysosomes).
Destination 2: the plasma membrane, 'the continuous secretion line'.
Vesicles containing biochemicals for continuous secretion menstruum to and fuse with the plasma membrane. This group of secretions will contribute to the biochemicals of the extracellular matrix, act as chemical signals to other cells, and provide proteins for the repair and replacement of the plasma membrane. This constitutive (or continuous) secretory pathway is also the default pathway. Products from the Golgi appliance non labelled for other routes use this line.
Destination 3: exterior the cell, 'the regulated secretion line'
Vesicles and chemicals of this group are produced in specialist secretory cells. They move from the trans Golgi network (TGN) towards the plasma membrane but accumulate in number earlier reaching the membrane.
Certain triggers will make the vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents in regulated bursts from the cell surface. Insulin release is an case of this when information technology is triggered past a rise in claret glucose level. Food intake is similar in that it triggers the release of mucus and digestive enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract.
Golgi and 'clones'
When a prison cell divides the Golgi apparatus, like the RER, breaks upward into modest fragments. These fragments are divided more or less evenly between the daughter cells. A new Golgi apparatus can merely grow from a fragment of Golgi apparatus from the previous jail cell, and so in that location is therefore the potential for a new Golgi apparatus to abound from each minor fragment. However, if in that location are no fragments there volition exist no Golgi apparatus. Without a Golgi apparatus the cell will non part.
Summary
-
The Golgi apparatus is a critical member of the biochemical manufacturing and supply chain inside a cell. Information technology receives biochemicals in a 'bulk catamenia' from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). It is the only organelle in the jail cell that receives, sorts, modifies, concentrates, packs and despatches biochemicals for use inside and outside the cell.
-
In specialist secretory cells the Golgi complex is responsible for the sorting and packing of such well-known items as insulin, digestive enzymes and pectin.
-
The Golgi apparatus produces specialist vesicles or vessels for the send of its products. Some of these take special wrappings or coatings that aid identify the contents. Some vesicles are recyclable.
-
Products from the Golgi apparatus go to three principal destinations:
(1) inside the cell to lysosomes (2) the plasma membrane (iii) outside the jail cell.
Source: https://bscb.org/learning-resources/softcell-e-learning/golgi-apparatus/#:~:text=Quick%20look%3A%20Golgi%20apparatus(or,close%20to%20the%20endoplasmic%20reticulum.
Posted by: martinposere88.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is The Golgi Body In Plant Or Animal"
Post a Comment